
| Key Takeaways: |
- RTDs vs. Thermistors: RTDs provide high accuracy across a broad temperature range, while thermistors are more sensitive with faster response times.
- Material and Cost: RTDs, made from platinum, are costlier and ideal for precise applications; thermistors use ceramics, offering a more affordable option.
- Temperature Range: RTDs operate from -200°C to 650°C, making them versatile, while thermistors are best suited for -100°C to 325°C applications.
- Application Fit: RTDs are perfect for industrial precision, while thermistors excel in consumer electronics and quick temperature monitoring tasks.
Understanding the Difference Between RTD and Thermistor: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to temperature measurement, choosing the right sensor is crucial for accuracy and performance. RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors) and thermistors are two commonly used temperature sensors, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the difference between RTD and thermistor is essential for selecting the appropriate sensor for your needs. This guide provides a detailed comparison to help you make an informed decision by highlighting the difference between RTD and thermistor in terms of their features, advantages, and best-use cases.
What is an RTD?
An RTD, or Resistance Temperature Detector, measures temperature by tracking how the RTD element’s resistance changes with temperature. RTDs are typically made from pure platinum, which ensures high accuracy and stability. The resistance of the RTD increases in a nearly linear manner with temperature, making it ideal for precise temperature measurements over a wide range.
Key Features of RTDs:
- Temperature Range: Operates effectively from -200°C to 650°C.
- Accuracy: Typically ranges from 0.1 to 1°C, offering high precision.
- Long-term Stability: Maintains stability with a change of about 0.05°C per year at 100°C.
- Linearity: Exhibits fairly linear resistance changes with temperature.
- Response Time: Generally slower, ranging from 1 to 50 seconds.
- Susceptibility to Electrical Noise: Rarely susceptible to electrical noise.
- Cost: Generally high due to the use of platinum and complex manufacturing.
Read Next: Types of RTD Sensors
What is a Thermistor?
A thermistor is a type of resistor with resistance that varies significantly with temperature. Thermistors, composed of ceramic materials, are available in two primary types: NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) and PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient). NTC thermistors decrease resistance as temperature increases, while PTC thermistors increase resistance with temperature. Thermistors are highly sensitive and are used in applications requiring precise temperature control.
Read on: The difference between NTC and PTC thermistor
Key Features of Thermistors:
- Temperature Range: Operates effectively from -100°C to 325°C.
- Accuracy: Typically ranges from 0.05 to 1.5°C, offering high sensitivity.
- Long-term Stability: Maintains stability with a change of about 0.2°C per year at 100°C.
- Linearity: Exhibits exponential resistance changes with temperature.
- Response Time: Fast, typically ranging from 0.12 to 10 seconds.
- Susceptibility to Electrical Noise: Rarely susceptible to electrical noise due to high resistance.
- Cost: Generally low to moderate, making it a more cost-effective option.
Key Differences Between RTD and Thermistor:
RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors) and thermistors are both commonly used temperature sensors, each with its unique characteristics and applications. While they both measure temperature by changes in electrical resistance, they differ significantly in their construction, temperature range, accuracy, response time, cost, and suitability for various applications. Let's delve into the key differences between RTDs and thermistors.
| Key Points | RTD | Thermistor |
| Materials and Construction | Primarily constructed from pure platinum, renowned for its exceptional stability and accuracy. The platinum wire is typically wound around a ceramic core for insulation and protection. | Manufactured from ceramic materials, often oxides of metals like manganese, nickel, or cobalt. These materials exhibit a significant change in resistance with temperature variations, making them highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. |
| Temperature Range | Operates effectively across a wide temperature range, typically from -200°C to 600°C. This versatility makes RTDs suitable for a broad range of applications, including industrial processes, scientific research, and laboratory environments. | While offering excellent sensitivity, thermistors are generally limited to a narrower temperature range, typically between -50°C and 150°C. This makes them more suitable for applications where temperature extremes are less common, such as consumer electronics, automotive sensors, and home appliances. |
| Accuracy | Known for its exceptional accuracy, RTDs are less susceptible to external factors like lead resistance, ensuring reliable and precise temperature measurements. | Although highly sensitive, thermistors may exhibit some variation in accuracy, especially at extreme temperatures. However, advancements in thermistor technology have improved their overall accuracy in recent years. |
| Response Time | RTDs generally have a slower response time due to their construction and mass. This can be a limitation in applications requiring rapid temperature measurements. | Thermistors are renowned for their fast response time, making them ideal for applications where quick temperature readings are essential, such as medical devices, process control, and automotive systems. |
| Cost | RTDs are typically more expensive than thermistors due to the cost of materials and manufacturing processes. The use of pure platinum and the precision involved in winding the wire contribute to the higher cost. | Thermistors are generally more cost-effective, especially for applications within their operational temperature range. The lower cost is attributed to the use of less expensive materials and simpler manufacturing techniques. |
| Applications | RTDs are commonly used in industrial processes, HVAC systems, and laboratory environments where high accuracy and a wide temperature range are critical. Examples include temperature control in furnaces, kilns, and chemical reactors. | Thermistors are ideal for consumer electronics, automotive sensors, and home appliances, where sensitivity and quick response are needed. They are commonly found in devices like thermostats, temperature sensors in refrigerators, and engine temperature gauges. |
JR Sensors: Mastering Precision in Temperature Measurement
JR Sensors is a trusted provider of high-quality thermistors designed to meet the diverse needs of industries such as automotive, healthcare, home appliances, and power electronics. Our thermistors are engineered with precision to ensure accurate temperature measurements, exceptional durability, and reliable performance in challenging environments. With a customer-centric approach, we offer tailored solutions to align with specific application requirements, ensuring optimal efficiency and satisfaction. Whether you need thermistors for EVs, industrial equipment, or consumer devices, JR Sensors is committed to delivering cutting-edge technology and unparalleled support to our valued customers.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between RTD and thermistor is key to selecting the right temperature sensor for your needs. RTDs are renowned for their accuracy and ability to measure across a broad temperature range, making them ideal for industrial and scientific applications. They provide reliable, precise measurements even in extreme conditions. On the other hand, thermistors offer rapid response times and high sensitivity, making them suitable for consumer electronics and applications where quick temperature changes are monitored. By considering factors like temperature range, accuracy, and response time, you can choose between RTDs and thermistors to ensure the best performance for your specific application.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main difference between RTD and thermocouples?
2. Where are RTDs and thermistors used?
3. What is the difference between RTD and PTC?
4. What is the difference between a thermistor and an LDR?
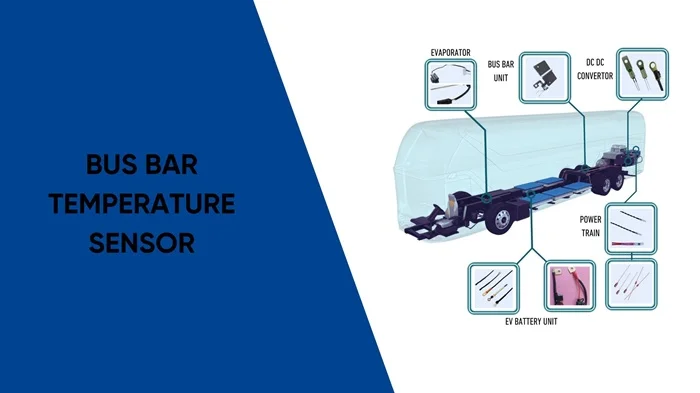
Busbar Watchdogs: The Tiny Sensors Preventing Massive Power Failures
Think of them as your system’s early warning system. Busbar temperature sensors silently protect power grids, data centers, and switchboards from overheating, fire, and failure. Discover why this small sensor plays a big role in electrical safety and uptime.

Beyond Specs: 5 Must-Know Factors When Choosing a Thermistor Sensor Manufacturer
Not all thermistor manufacturers are created equal. Whether you're building a medical device or a smart appliance, this guide breaks down the 5 key factors that ensure you get precision, reliability, and peace of mind.

Burnt Biscuits? Blame the Sensor – The Hot Truth About Your Oven’s Temperature Troubles
If your oven’s cooking like it’s got a mind of its own, your temperature sensor might be the silent saboteur. From half-baked casseroles to scorched cookies, we break down how this little sensor works, why it matters, and how to fix it—without losing your cool (or your dinner). A fun, practical guide that’s just as useful as it is digestible.