Applications and Advantages of NTC Temperature Sensors in Electronics
Applications and Advantages of NTC Temperature Sensors in Electronics

NTC devices let your phone tell you when it’s become hot. That’s driven by an NTC thermistor acting in the background. NTC thermistor, short for Negative Temperature Coefficient, gets less resistant as the temperature increases (same as when we’re sleepy on a Monday morning). Such components play a key role in modern electronics by quietly controlling temperature in smartphones, electric vehicles and medical tools. NTC thermistors have uses for engineers, those who like tech, and even people who just wish their gadgets stayed cool, so learning about them can be fun and practical.
What is an NTC Thermistor?
You need to know that NTC refers to the Negative Temperature Coefficient first. An NTC thermistor’s resistance goes down as the temperature goes up and vice versa. That's why it is important in electronic products and assemblies.
How Do NTC Thermistors Work?
NTC thermistors are designed from special semiconductor materials that see their resistance drop as the temperature goes up. When the material heats up, more electrons are activated, which helps the device carry current more freely. NTC thermistors are very useful in areas where temperature matters because their resistance always changes predictably. Thanks to their rapid and precise temperature response, they serve as good sensors in many kinds of electronics. Protecting the battery in a smartphone or electric car is just like tracking vital signs in medical machinery; their sensors make sure that everything remains within safe levels. The reason why engineers enjoy them is how easy, reliable and versatile they are. Therefore, thanks to NTC thermistors, both your coffee and your laptop won’t overheat as you watch more episodes late at night.
Applications of NTC Thermistors in Electronics
NTC thermistors are versatile components used across various industries:
- Consumer Electronics: Devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearable technology use NTC thermistors for thermal management, preventing overheating and optimising performance.
- Automotive Industry: NTC thermistors monitor engine coolant and oil temperatures, ensuring optimal engine performance.
- Medical Devices: In medical equipment such as incubators and dialysis machines, NTC thermistors ensure precise temperature control, critical for patient safety.
- HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems use NTC thermistors for accurate temperature regulation and energy efficiency.
- Battery Management: NTC thermistors are employed in battery packs to monitor temperature variations, preventing overheating and extending battery life.
Advantages of Thermistors
NTC thermistors offer several benefits:
- High Sensitivity: They can detect minute changes in temperature, making them ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control.
- Compact Size: Their small size allows for integration into space-constrained devices.
- Cost-Effective: NTC thermistors offer high performance at a low cost, making them a preferred choice for various industries.
- Wide Operating Temperature Range: They function effectively across a broad temperature range, suitable for diverse applications.
- Rapid Response Time: NTC thermistors exhibit a rapid response to temperature changes, ensuring real-time monitoring and quick adjustments in electronic systems.
Other NTC Thermistors Applications
Beyond conventional uses, NTC thermistors find applications in:
- Renewable Energy Systems: They monitor and manage the temperature of solar panels and inverters, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal energy conversion.
- Aerospace Technology: NTC thermistors are used for temperature monitoring in critical systems such as avionics and environmental control systems.
- Telecommunication: They stabilise the temperature of electronic NTC circuits in telecommunication equipment, ensuring reliable data transmission.
- Consumer Goods: NTC thermistors are integral in managing and controlling temperatures in household appliances like coffee makers, electric kettles, and hairdryers.
Benefits of NTC Thermistor Chips
NTC thermistor chips offer specific advantages:
- Miniaturisation: Their small size allows for integration into compact electronic devices.
- High Reliability: They provide consistent performance over time, essential for critical applications.
- Ease of Integration: NTC thermistor chips can be easily incorporated into various circuit designs.
How to Choose the Right NTC Thermistor Chip
When selecting an NTC thermistor chip, consider the following factors:
- Temperature Range: Ensure the thermistor operates effectively within the desired temperature range.
- Resistance Value: Choose a thermistor with an appropriate resistance value for your application.
- Tolerance: Consider the acceptable deviation in resistance value to ensure accuracy.
- Response Time: Select a thermistor with a response time suitable for your application's requirements.
- Packaging: Choose a package type that fits your design and environmental conditions.
Conclusion
NTC thermistors are vital to modern electronics because they precisely measure and control temperatures in many ways. The special qualities of their sensitivity, small size and low cost help them stand out in industries such as consumer electronics and aerospace. When engineers and designers comprehend how NTC thermistors working principle are and where to apply them, their systems perform well and efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an NTC temperature sensor?
2. What does NTC stand for in electronics?
3. Where are NTC thermistors commonly used?
4. What are the advantages of using NTC thermistors?
5. How do I choose the right NTC thermistor chip?
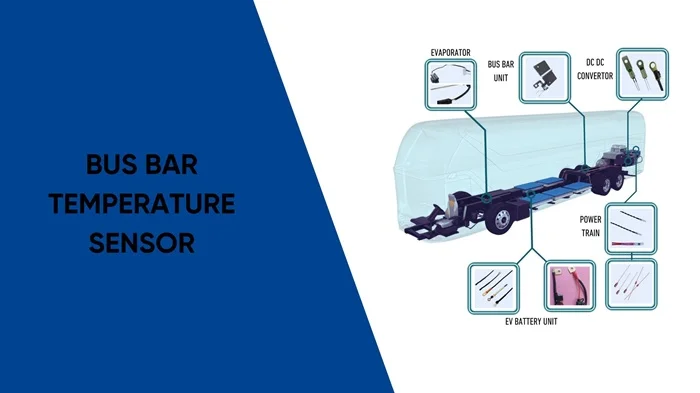
Busbar Watchdogs: The Tiny Sensors Preventing Massive Power Failures
Think of them as your system’s early warning system. Busbar temperature sensors silently protect power grids, data centers, and switchboards from overheating, fire, and failure. Discover why this small sensor plays a big role in electrical safety and uptime.

Beyond Specs: 5 Must-Know Factors When Choosing a Thermistor Sensor Manufacturer
Not all thermistor manufacturers are created equal. Whether you're building a medical device or a smart appliance, this guide breaks down the 5 key factors that ensure you get precision, reliability, and peace of mind.

Burnt Biscuits? Blame the Sensor – The Hot Truth About Your Oven’s Temperature Troubles
If your oven’s cooking like it’s got a mind of its own, your temperature sensor might be the silent saboteur. From half-baked casseroles to scorched cookies, we break down how this little sensor works, why it matters, and how to fix it—without losing your cool (or your dinner). A fun, practical guide that’s just as useful as it is digestible.