
Types of Temperature Sensors Used in HVAC Systems | Comprehensive Guide
Types of Temperature Sensors Used in HVAC Systems | Comprehensive Guide

Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are essential for creating comfortable indoor environments in residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. To operate efficiently and maintain optimal conditions, HVAC systems rely on a variety of sensors. These sensors monitor and regulate parameters such as temperature, humidity, pressure, and air quality. Among these, temperature sensors play the most crucial role as they directly impact heating and cooling functions.
This guide delves into the temperature sensors used in HVAC systems, highlighting JR Sensors’ contributions, and briefly lists other types of sensors used in HVAC applications.
Introduction to Sensors in HVAC
Sensors are integral to HVAC systems, providing real-time data to ensure efficient operation. Without sensors, maintaining precise temperature control, energy efficiency, and system safety would be nearly impossible. Temperature sensors, in particular, form the backbone of HVAC systems as they regulate heating and cooling cycles, maintaining consistent indoor temperatures.
Temperature sensors play a vital role in HVAC systems, ensuring efficient operation and maintaining comfortable indoor environments. These are the main type of sensors in HVAC that perform three key functions:
1. Monitor Air Temperature
Temperature sensors continuously monitor the air temperature in HVAC systems, providing critical data for maintaining desired indoor conditions. They are typically placed in rooms, ducts, or outdoor units to measure ambient temperatures. The system uses this data to adjust heating or cooling cycles, ensuring energy efficiency and optimal comfort. For example, in a residential HVAC system, air temperature sensors detect fluctuations and signal the thermostat to activate heating or cooling units as needed.
2. Measure Refrigerant Temperatures
In HVAC systems, refrigerants are responsible for transferring heat to regulate indoor temperatures. Temperature sensors monitor the refrigerant's temperature at various points in the system, such as the evaporator, condenser, or compressor. This ensures the refrigerant remains within its optimal operating range, preventing issues like overheating, freezing, or system inefficiency.
3. Track Surface Temperatures in Ducts and Coils
Surface temperature sensors are often used to monitor the temperatures of ducts, pipes, and coils. Accurate surface temperature readings are essential for ensuring the efficient transfer of heat and maintaining consistent air distribution. These sensors help detect issues such as coil icing or duct heat loss, allowing timely maintenance and preventing energy wastage.
With advancements in sensor technology, specialized solutions like those from JR Sensors are setting new benchmarks in accuracy and reliability.
Different Types of Temperature Sensors Used in HVAC
Temperature sensors in HVAC are designed to measure and control temperatures in various system components. Below are the main types of temperature sensors commonly used in HVAC systems:
1. Thermistors
Thermistors are highly sensitive temperature sensors that provide precise readings. They are available in two types:
- Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Thermistors: Resistance decreases as temperature rises.
- Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) Thermistors: Resistance increases with temperature.
In HVAC systems, NTC thermistors are commonly used for monitoring ambient air temperatures due to their accuracy and responsiveness.
2. Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
RTDs are known for their precision and stability over a wide temperature range. They work by measuring resistance changes in a metal, typically platinum, as temperature varies. RTDs are often used in critical HVAC applications that require high accuracy, such as in industrial systems.
3. Thermocouples
Thermocouples are versatile sensors that measure temperature by generating a voltage in response to temperature differences between two dissimilar metals. They are durable and suitable for extreme temperature environments, such as monitoring refrigerant temperatures or furnace operations.
4. Infrared (IR) Sensors
Infrared temperature sensors measure surface temperatures without direct contact. They are ideal for HVAC applications that require monitoring of hard-to-reach areas, such as ducts or heat exchangers.
JR Sensors
JR Sensors specializes in advanced temperature sensing solutions tailored for HVAC applications. These sensors are designed for precision, durability, and ease of integration. JR Sensors provides a range of products, including:
- Duct Temperature Sensors: Ideal for monitoring air temperatures within ducts.
- Immersion Temperature Sensors: Used to measure liquid temperatures in HVAC systems.
- Surface Temperature Sensors: Designed for applications requiring contact temperature readings on pipes or coils.
- Wireless Temperature Sensors: Offering flexibility and reduced installation time for modern HVAC systems.
The innovation and reliability of JR Sensors make them a preferred choice for HVAC professionals looking for accurate temperature control solutions.
Other Types of Sensors Used in HVAC
While temperature sensors are critical, HVAC systems also rely on other sensors to monitor various environmental and system parameters. Below is a list of other sensors used in HVAC applications:
- Humidity Sensors: Measure moisture levels in the air to maintain indoor air quality.
- Pressure Sensors: Monitor airflow, refrigerant pressure, and duct pressure for efficient system operation.
- Air Quality Sensors: Detect pollutants, carbon dioxide (CO2), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in indoor spaces.
- Occupancy Sensors: Detect room occupancy to optimize energy use by adjusting heating or cooling.
- Flow Sensors: Measure the flow rate of air or liquid within the HVAC system.
- Light Sensors: Used in advanced HVAC systems to integrate lighting control with heating and cooling.
- Motion Sensors: Identify movement in a room for energy-saving automation.
- Sound Sensors: Monitor noise levels within HVAC systems to detect malfunctions.
While these sensors play an important role, the efficiency of HVAC systems largely depends on the performance of temperature sensors.
Conclusion
Sensors are the backbone of any HVAC system, enabling precise monitoring and control of various parameters. Among all sensors, temperature sensors are indispensable for regulating heating and cooling functions. Advanced temperature sensors, like those from JR Sensors, provide superior accuracy, reliability, and durability for HVAC applications. Whether you need duct, immersion, or wireless temperature sensors, JR Sensors offers state-of-the-art solutions tailored to meet modern HVAC system demands.
By choosing JR Sensors, you can ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and a comfortable indoor environment for your HVAC systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What role do temperature sensors play in HVAC systems?
2. What makes JR Sensors stand out in the HVAC industry?
3. Are thermocouples better than thermistors for HVAC applications?
4. What are duct temperature sensors used for?
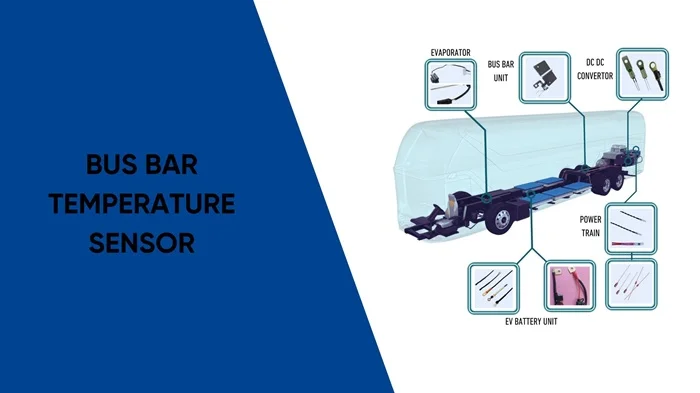
Busbar Watchdogs: The Tiny Sensors Preventing Massive Power Failures
Think of them as your system’s early warning system. Busbar temperature sensors silently protect power grids, data centers, and switchboards from overheating, fire, and failure. Discover why this small sensor plays a big role in electrical safety and uptime.

Beyond Specs: 5 Must-Know Factors When Choosing a Thermistor Sensor Manufacturer
Not all thermistor manufacturers are created equal. Whether you're building a medical device or a smart appliance, this guide breaks down the 5 key factors that ensure you get precision, reliability, and peace of mind.

Burnt Biscuits? Blame the Sensor – The Hot Truth About Your Oven’s Temperature Troubles
If your oven’s cooking like it’s got a mind of its own, your temperature sensor might be the silent saboteur. From half-baked casseroles to scorched cookies, we break down how this little sensor works, why it matters, and how to fix it—without losing your cool (or your dinner). A fun, practical guide that’s just as useful as it is digestible.